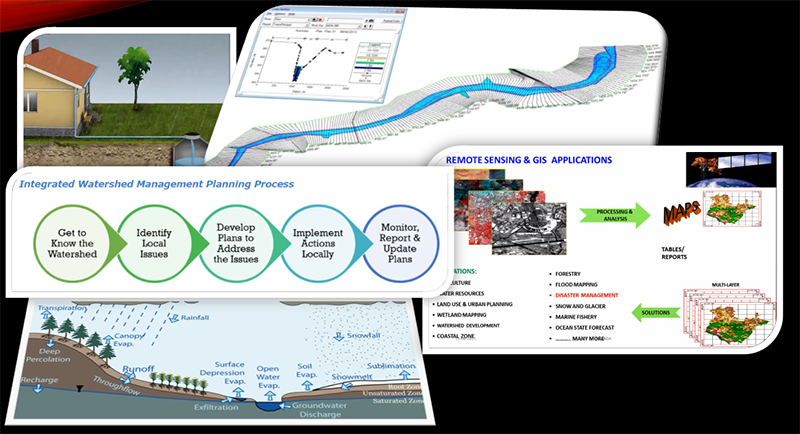
The Soil and Water Conservation through Watershed domain provides fundamental knowledge of statistical analysis of hydrological data along with visualization of the data using R-programming and Geo-spatial application in watershed management using ArcGIS software. The students will have knowledge of various rainwater harvesting structures, techniques for Integrated watershed management and hand-on practices on hydrological models such as SWAT and HEC-RAS for simulated watershed processes.
Domain Track: Soil and Water Conservation through Watershed
Course Attendees
Still no participant
Course Reviews
Still no reviews
Track Total Credits (T-P-P): (4-11-13) 28 Credits
Courses Division (list all divisions):
- Rainwater Harvesting and Artificial Recharge (CUSW2340) (1-2-0)
- Integrated watershed management (CUSW2341) (2-1-0)
- Sustainable Watershed (CUSW2342) (1-2-0)
- R programming in watershed hydrology (CUSW2343) (0-2-1)
- Modelling and Simulation of Watershed Processes (CUSW2344) (0-2-1)
- Geo-spatial application in watershed management (CUSW2345) (0-2-1)
- Industrial internship (CUSW2346) (0-0-10)
Domain Track Objectives:
The Soil and Water Conservation through Watershed domain builds skills in collecting, analyzing, and critically evaluating hydro-meteorological data and watershed data from multiple sources. It is taught through an engaging hands-on learning method that starts with fundamental theoretical foundations and progresses to understanding how to use hydrological modelling and geospatial applications to manage any watershed. This domain will encourage students to engage in research and build capabilities in managing multi-disciplinary field projects.
- Build skills in collecting, analyzing, and critically evaluating watershed data and documents from multiple sources
- Apply hydrological modelling along with Geospatial application to manage the watershed
- Improving livelihoods in rainfed areas through integrated watershed management
- Pursue research and develop capabilities to handle multi-disciplinary field projects
Domain Track Learning Outcomes:
- Analyzing and visualization of watershed data using R Programming
- Application of different hydrological models to simulate watershed process
- Application of rainwater harvesting in an integrated watershed management approach
- Application of geospatial tools and environment to achieve project objectives
Career Scope:
- Water resource Engineer
- Watershed manager
- GIS Engineer
- Higher studies and Research
- Self-employment through entrepreneurship
Domain Syllabus:
Rainwater Harvesting and Artificial Recharge - CUSW2340 (1-2-0)
Theory
Rain water harvesting – definition and scope of rainwater harvesting; history of rainwater harvesting; need and importance of rainwater harvesting; components of rainwater harvesting; Hydrological aspects of water harvesting - hydrological cycle and water balance; hydrological characteristics; factors affecting runoff; runoff models suitable for water harvesting; Identification of areas suitable for water harvesting - parameters for identifying; suitable areas; methods of data acquisition; tools available; Different types of water harvesting structures - Negarim micro-catchments; contour bunds for trees; semi-circular bunds; contour ridges for crops; trapezoidal bunds; contour stone bunds; permeable rock dam; water spreading bunds; Runoff Inducement Methods; Roof water harvesting components and layout; Farm pond – types of farm ponds; embankment type; excavated or dugout ponds; site selection for dugout type farm ponds; Design of farm pond, Design of earthen embankment; Illustrate the importance of repair and maintenance of water harvesting structures; Artificial recharge techniques – direct and indirect methods; Economic indicator - Net present value; benefit cost-ratio; internal rate of return; payback period.
Practice
Study of hydrological cycle and water balance; Studying runoff models suitable for water harvesting; Methods of data acquisition; Computation of trapezoidal bund requirement per hector; General design considerations for earth dam; Computing design or dependable catchment yield; Design of farm pond; Design of earthen embankment; Calculation of roof water harvesting and water harvesting potential; Design of storage tank capacity for roof-top rainwater harvesting; Analysis of causes of failure of earthen bund; Analysis of causes of failure of earthen embankment; Slices method of stability analysis; Foundation stability against shear; Calculation of roof water harvesting and water harvesting potential; Design of storage tank capacity for roof-top rainwater harvesting; Determination of phreatic line in earthen dam – graphical and analytical method; Case study for showing economic evaluation of recharge schemes; Operation and maintenance of water harvesting structures; Analyse the cost benefit of a water harvesting structures.
Integrated watershed management- CUSW2341 (2-1-0)
Theory:
Watershed definitions, Components, Coding of watershed, Familiarization with the watershed problems; Topographical survey, Morphometric analysis of watershed, Factors affecting watershed processes Delineation of watershed, Prioritization of watershed, Watershed response to land use; Storm water management, Flood management, drought management; Watershed development plan for rain-fed areas; Policies for IWM, Institutional activities on integrated watershed management; Tools for improved IWM practice; Review of Integrated Watershed Management Program in India.
Practice
Visualization of different geo-spatial tools used in IWM; Introduction to various open-source geo-spatial data repositories; Representation of earth features in GIS; Delineation of catchment area using Arc-GIS; Basic morphometric analysis of watershed; Preparation of Thiessen polygon to compute areal precipitation; Preparation of spatial maps of different watershed components; Environmental flow assessment; Identification of potential sites for conservation structure implementation; Field visit for working knowledge on different adaptive options on watershed management; Understanding of past successful IWM programs.
Sustainable Watershed- CUSW2342 (1-2-0)
Theory
History, development and national importance of watershed programs; Principles and objectives of watershed; Introduction to the concept of sustainable watershed management; Principles of sustainable watershed management; Natural resources management and different case Study; Hydrologic modelling for sustainable watershed management; Hydrologic modelling related case studies; Watershed health and sustainability; Water law and policy; Ecosystem services; Floods - causes of occurrence, flood classification - probable maximum flood, standard project flood, design flood; Flood control-history of flood control, structural and non-structural measures of flood control, storage and detention reservoirs, levees, channel improvement. Flood routing.
Practice
Hydrologic modelling for sustainable watershed management using GIS approach; Identification of recharge areas using remotely sensed data; Erosion, erodibility & sediment yield modelling; Reservoir sedimentation estimation using GIS and remote sensing; Introduction to HEC-HMS model; Simulation through HEC-HMS model; Practice on HEC-HMS model; Flood estimation-methods of estimation; flood frequency methods – log normal, Gumbel’s extreme value; Flood routing related basic equations; Hydrologic storage routing method: Modified Pul’s method; Hydrologic storage routing method: Goodrich method; Hydrologic channel routing: Muskingum equation; Introduction to 1D river modelling; Simulation of flood model; Overview of 2D modelling and difference between 1D and 2D flood modelling.
R programming in watershed hydrology- CUSW2343 (0-2-1)
Practice
Programming Language: basic definition and terms; Introduction to R programming; Basic syntax in R-programming; A first R session; Working with Data in R; Data type in R; R-Functions and R-strings; R-vector, R-Lists; R-Matrix, R array; R-factors, R-Dataframes; R – Packages, R – Csv Files and R – Excel File; R – Scatterplots, R – Line Graphs and R – Histograms; R – Boxplots, R – Bar Charts and R – Pie Charts; R – Linear Regression, R – Multiple Regression and R – Logistic Regression; R – Normal Distribution, R – Binomial Distribution; Creating Confidence Intervals, Performing t Tests; R – Poisson Regression, R – Analysis of Covariance and R – Time Series Analysis; R – Nonlinear Least Square and R – Chi Square Test; Nonparametric Tests in R; R- Simple Hypothesis Testing; R for Simulation; The “New” Statistics: Resampling and Bootstrapping; Making an R Package; R in hydrology: a review of recent developments; R-Packages for retrieving hydro-meteorological data; R-Packages for reading, manipulating, and cleaning the data; R-Packages for extracting driving data, spatial analysis, and cartography; R-Packages for hydrological statistics; R-Packages for static and dynamic hydrological data visualization.
Modelling and simulation of watershed processes- CUSW2344 (0-2-1)
Practice
Brief introduction on watershed processes, importance of modeling and simulation of watershed processes; Introduction and installation of SWAT model and overview of data requirements ; Watershed delineation, HRU analysis; Simulation through SWAT model (calibration); Simulation through SWAT model (validation); Introduction and installation of SPAW model and overview of data requirements; Simulation through SPAW model (calibration); Practice class for simulation with SWAT and SPAW; HEC-RAS model: Introduction and overview of model, installation; Simulation through HEC-RAS model; HBV model: Introduction and overview of model, installation; Simulation through HBV model; Practice class for simulation with HEC-RAS and HBV; Introduction to TOP model and installation; Simulation through TOP model; DSS-ET model: Introduction and overview; Installation, Simulation with DSS-ET model; Case studies with different hydrological models.
Geo-spatial application in watershed management- CUSW2345 (0-2-1)
Practice
Installation of Arc GIS; Downloading of maps and imageries from online repositories; Basic GIS operations in ARC GIS; Representation of earth features in GIS; Working with satellite imageries; Geo-referencing of satellite image; Preparation of contour map in ARC GIS; Preparation of slope and aspect map of watershed; Introduction to google earth; Google earth application as a ground truth tool; Supervise LULC classification; Un-supervise LULC classification; Preparation of drainage density map and stream ordering; Watershed delineation using DEM; Mapping of soil erosion; Identification of potential locations for groundwater recharge; River flow path analysis; Evapotranspiration mapping using MODIS product; Water budget analysis using ARC GIS.
Session Plan for the Entire Domain:
- 1.1. Water Harvesting – concepts, methods;
- 1.2. Soil’s requirement for water harvesting;
- 1.3. Design model for catchment: cultivated area ratio
- 1.4. Site and technique selection for WHS;
- 1.5. Different types of water harvesting structures;
- 1.6. Computation of trapezoidal bund per hector
- 1.7. In-situ rainwater harvesting – advantages and methods;
- 1.8. Roof water harvesting components and layout;
- 1.9. Calculation of roof water harvesting and water harvesting potential;
- 1.10. Farm pond – uses and types; Earthen dam – types and design criteria;
- 1.11. Design of farm pond, Design of earthen bund;
- 1.12. Analysis of causes of failure of earthen bund;
- 1.13. Determination of phreatic line in earthen dam – graphical and analytical method
- Youtube: Earthern Dam-MGNREGA ...

- Youtube: Earthern Dam-MGNREGA ...
- 1.14. Illustrate the importance of repair and maintenance of WHS;
- 1.15. Artificial recharge techniques – direct and indirect methods;
- 1.16. Design of storage tank capacity for roof-top rainwater harvesting
- 1.17. Case study for showing economic evaluation of recharge schemes.
- 1.18. Analyse the cost benefit of a WHS
- 2.1. Introduction: watershed definitions; why a watershed approach;
- 2.2. watershed response to land use; watershed analysis approach;
- 2.3. history of watershed management; Current Issues in Water Management;
- 2.4. Characteristics of Effective Watershed Management; Why "Integrated" Management?; Objectives of IWM;
- 2.5. Recommend Planning and Management Approach;
- 2.6. Improving livelihoods in rainfed areas through integrated watershed management: A development perspective;
- 2.7. Watershed development for rainfed areas: Concept, principles, and approaches;
- 2.8. Equity in watershed development: Imperatives for property rights, resource allocation, and institutions;
- 2.9. Policies and institutions for increasing benefits of IWM programs;
- 2.10. Application of tools in IWM for enhancing impacts;
- 2.11. Impact of watershed projects in India: Application of various approaches and methods;
- 2.12. Watershed management through a resilience lens; Review of Integrated Watershed Management Programme-2009-10 in India,
- 2.13. Review of case studies on IWP in Maharashtra, Jharkhand, Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh.
- 2.14. Advances in Geospatial Technologies in IWM;
- 2.15. GIS-Based monitoring systems for IWM;
- 2.16. Identify catchment area and command area;
- 2.17. Concepts of environmental flow assessment and methods with examples and case studies;
- 2.18. Planning and Design of Shelter belt for checking soil erosion in watershed;
- 2.19. Calculation of effective precipitation for watershed;
- 2.20. Field visits; Step by step processes in IWM planning and implementation strategy.
- 3.1. History, development and national significance of watershed programmes;
- 3.2. principles and objectives of watershed;
- 3.3. Different participatory watershed management approaches;
- 3.4. Estimation of soil loss (USLE)
- 3.5. Characteristics of watershed management role of a Watershed Consultant;
- 3.6. Introduction to the concept of sustainable watershed management;
- 3.7. Principles of sustainable watershed management;
- 3.8. Measurement of soil loss (multi slot divisor)
- 3.9. Natural resources management and different case Study.
- 3.10. Study of grassed waterways
- 3.11. Study of contour bund and compartmental bunding
- 3.12. Study of terraces
- 3.13. Study of CCT and staggered trenches
- 3.14. Study of gully plug, nala bund, check dams and K.T.weirs
- 3.15. Hydrologic modelling for sustainable watershed management and related case studies
- 3.16. Hydrologic modelling for sustainable watershed management and related case studies-GIS approach
- 3.17. Determination of pond capacity
- 3.18. Identification of recharge areas using remotely sensed data
- 3.19. Watershed health and sustainability;
- 3.20. Erosion, erodibility & sediment yield modelling
- 3.21. Water law and policy;
- 3.22. Ecosystem services.
- 3.23. Reservoir sedimentation estimation using GIS and RS
- 3.24. Visit to watershed
- 4.0. Introducing R: What It Is and How to Get It;
- Webpage: Download RStudio
- Webpage: Download and Install R
- Video: Installing R on a Mac
- Video: Installing R Studio (Mac)
- Video: Install R and R Studio on Windows 10
- Video: Writing Code / Setting Your Working Directory (Windows)
- Video: Writing Code / Setting Your Working Directory (Mac)
- 4.1 Programming Language: basic definition and terms
- 4.2 Introduction to R programming
- Video: Introduction-R ...

- Video: Introduction-R ...
- 4.3 Basic syntax in R-programming
- Video: Basic syntax in R ...

- Video: Basic syntax in R ...
- 4.4 A first R session
- 4.5 Working with Data in R
- 4.6 Discussion regarding project work
- 4.7 Data type in R
- 4.8 Discussion regarding project work
- 4.9 Variable, Operators, decision making and loops
- Video: R Programming - Variables ...

- Video: R-Operator ...

- Video: R-Decision making ...
 , if Statement ...
, if Statement ... , if else Statement ...
, if else Statement ... , Switch Statement ...
, Switch Statement ...
- Video: for Loop ...
 , While Loop ...
, While Loop ... , Repeat Loop ...
, Repeat Loop ...
- Video: R Programming - Variables ...
- 4.10 R-Functions and R-strings
- 4.11 R-vector, R-Lists
- Video: Create and Name Vectors in R ...

- Video: Create & Name Lists in R ...

- Video: Create and Name Vectors in R ...
- 4.12 R-Matrix, R array
- Video: How to Create and Name Matrices in R ...

- Video: Array in R ...

- Video: How to Create and Name Matrices in R ...
- 4.13 R-factors, R-Dataframes
- Video: Using Factors in R ...

- Video: Using the Data Frame in R ...

- Video: Using Factors in R ...
- 4.14 Discussion with students regarding doubts
- 4.15 1st Internal class test
- 4.16 R – Packages, R – Csv Files and R – Excel File
- 4.17 R – Scatterplots, R – Line Graphs and R – Histograms
- 4.18 R – Boxplots, R – Bar Charts and R – Pie Charts
- 4.19 R – Linear Regression, R – Multiple Regression and R – Logistic Regression
- 4.20 R – Normal Distribution, R – Binomial Distribution
- 4.21 Creating Confidence Intervals, Performing t Tests
- 4.22 R – Poisson Regression, R – Analysis of Covariance and R – Time Series Analysis
- 4.23 R – Nonlinear Least Square and R – Chi Square Test
- 4.24 Nonparametric Tests in R
- 4.25 R- Simple Hypothesis Testing
- 4.26 R for Simulation
- 4.27 The “New” Statistics: Resampling and Bootstrapping
- 4.28 Making an R Package
- 4.29 R in hydrology: a review of recent developments
- 4.30 R-Packages for retrieving hydro-meteorological data_1
- 4.31 R-Packages for retrieving hydro-meteorological data_2
- 4.32 R-Packages for reading, manipulating, and cleaning the data
- 4.33 R-Packages for extracting driving data, spatial analysis, and cartography_1
- 4.34 R-Packages for extracting driving data, spatial analysis, and cartography_2
- 4.35 R-Packages for hydrological statistics
- 4.36 R-Packages for static and dynamic hydrological data visualization_1
- 4.37 R-Packages for static and dynamic hydrological data visualization_2
- 4.38 R-Packages for creating presentations and documents
- 4.39 Discussion with students regarding doubts
- 4.40 2nd Internal Exam
- 5.1. Soil-Plant-Air-Water (SPAW) model: model overview, Data requirement, Simulation, Calibration and Sensitivity;
- 5.2. Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT): Installation of ARCSWAT and other associated software,
- Youtube: How to Install ArcSWAT ...

- Youtube: How to Install ArcSWAT ...
- 5.3. Project Setup, Watershed delineation, HRU analysis,
- Youtube: Make a SWAT Model ...

- Youtube: ArcSwat- Watershed Delineation ...

- Youtube: ArcSwat - HRU summary ...

- Youtube: Make a SWAT Model ...
- 5.4. Weather Definition, Edit SWAT inputs,
- Youtube: ArcSwat - Weather ...

- Youtube: ArcSwat - Weather ...
- 5.5. SWAT Simulation,
- Youtube: ArcSwat - Run the Model ...

- Youtube: ArcSwat - Run the Model ...
- 5.6. Calibration and Validation of SWAT Model;
- 5.7. HEC-HMS model: Data Requirements,
- Youtube: How to Set up HEC HMS Model ...

- Youtube: How to Set up HEC HMS Model ...
- 5.8. project setup, Hydrologic Elements,
- 5.9. Editing a Basin Model, Creating a Meteorological Model,
- 5.10. Defining the Control Specifications, Executing the HMS Model,
- Youtube: HEC HMS Hydrologic Modeling ...

- Youtube: HEC HMS Hydrologic Modeling ...
- 5.11. Evaluation of model results;
- 5.12. Storm Water Management Model (SWMM): Overview of the model,
- 5.13. project setup, drawing objects,
- Youtube: SWMM Example ...

- Youtube: SWMM Example ...
- 5.14. Setting Object Properties,
- Youtube: SWMM Example ...

- Youtube: SWMM Example ...
- 5.15. Running a simulation,
- Youtube: Simulation of SWMM ...

- Youtube: Simulation of SWMM ...
- 5.16. Viewing Results on the Map,
- Youtube: Analysis of SWMM ...

- Youtube: Analysis of SWMM ...
- 5.17. Resizing the Network.
- Youtube: Sizing pipes ...

- Youtube: Sizing pipes ...
- 6.1. Interpretation of aerial photographs and satellite imageries: resolution mosaics symbols,
- 6.2. Gully pattern and drainage analysis, vertical exaggeration and image distortion;
- 6.3. Analysis of Aerial photographs and satellite images for drainage morphometry and watershed demarcation;
- 6.4. Analysis of satellite and aerial photographs for surface water resources mapping;
- 6.5. Analysis of satellite and aerial photographs for mapping Lithologically and structurally controlled aquifer systems;
- 6.6. Mapping of geomorphic aquifers;
- 6.7. Identification of recharge areas using remotely sensed data;
- Youtube: Aquifer recharge estimation ...

- Youtube: Aquifer recharge estimation ...
- 6.8. Applications of Digital Elevation Models in Water Resources;
- Youtube: Digital Elevation Models in GIS ...

- Youtube: Digital Elevation Models in GIS ...
- 6.9. Erosion, Erodibility & Sediment Yield Modeling;
- 6.10. Ground water exploration using remote sensing techniques and preparation of theme based maps, pre-field interpretation and field checks;
- 6.11. Analysis of thermal and microwave data for ground water Targeting;
- 6.12. Land use/land cover mapping up to level II using aerial photos and satellite images;
- Youtube: Land Use Land Cover Mapping ...

- Youtube: Land Use Land Cover Mapping ...
Reference Books
- Pourghasemi, H. R., & Gokceoglu, C. (Eds.). (2019). Spatial modeling in GIS and R for earth and environmental sciences. Elsevier.
- Kennedy, M. D. (2013). Introducing geographic information systems with ARCGIS: a workbook approach to learning GIS. John Wiley & Sons.
- Gonenc, I. E., Wolflin, J. P., & Russo, R. C. (Eds.). (2014). Sustainable Watershed Management. CRC Press.
- Wani, S. P., Rockstrom, J., & Sahrawat, K. L. (2011). Integrated watershed management in rainfed agriculture. CRC Press.
- Beheim, E., Rajwar, G. S., Haigh, M., & Krecek, J. (Eds.). (2012). Integrated watershed management: perspectives and problems. Springer Science & Business Media.
- Mailund, T. (2017). Advanced Object-Oriented Programming in R: Statistical Programming for Data Science, Analysis and Finance. Apress.
Media

Our Main Teachers

Subhankar Debnath is currently working as Assistant Professor in the Department of Agricultural Engineering at Centurion University of Technology and Management, Odisha. His research interests include Agricultural water management, Climate Change, Crop modeling and Internet of things (IoT). He has completed M.Tech in Land and Water Resources Engineering from IIT Kharagpur and B.Tech in Agricultural […]

Dr. Santosh D.T is currently working as Assistant Professor in the Department of Agricultural Engineering at Centurion University of Technology and Management, Odisha. He has completed Ph.D. in Land and Water Resources Engineering from IIT Kharagpur. Prior to joining as assistant Professor, he hadworked as Research Associate in Precision Farming Development Centre, IIT Kharagpur, Sponsored […]