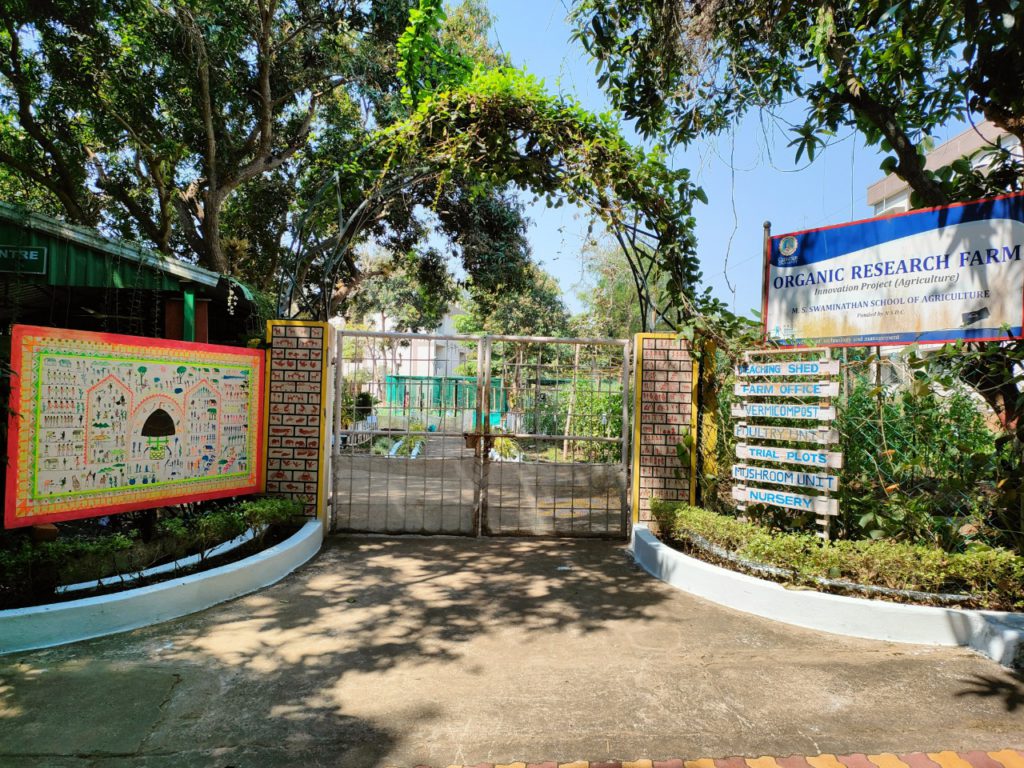
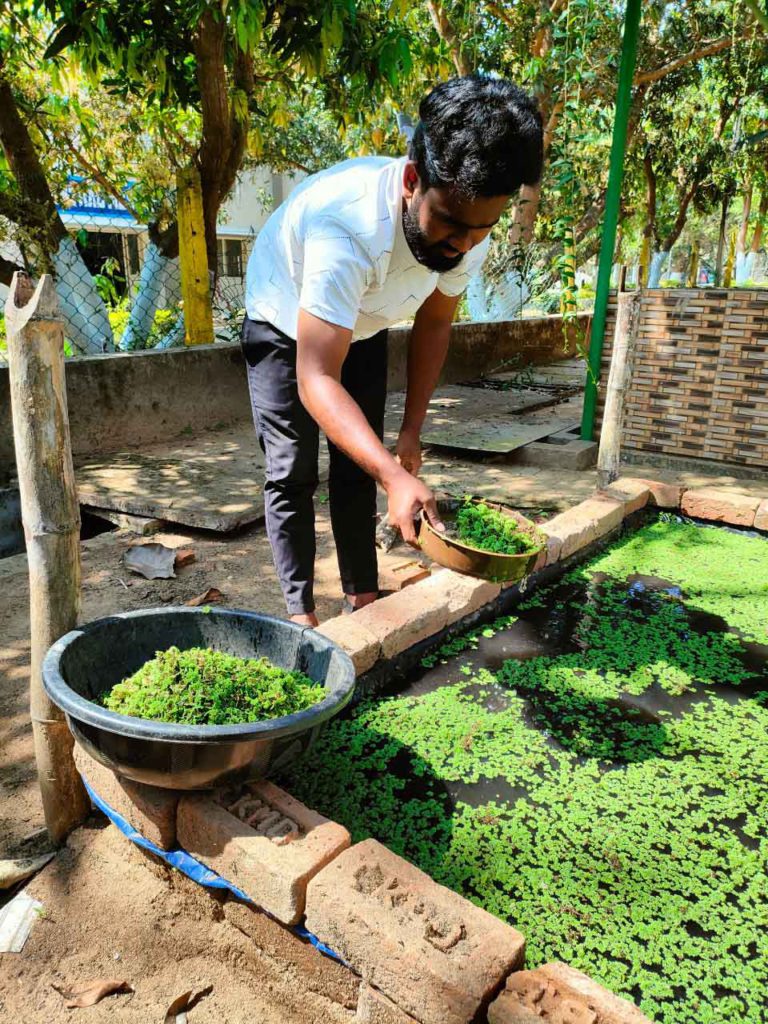
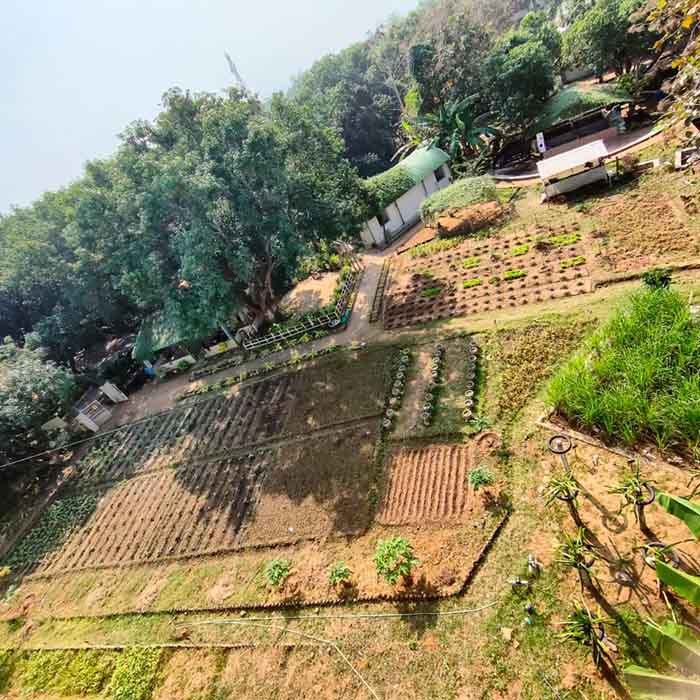
Domain organic farming is designed to impart skill and practical knowledge to students for production of quality organic produce adhering to organic certification standard protocol and sale of the produce obtained through appropriate marketing channel that fetches premium market price. The course deals with production of field and horticultural crops under organic management. Moreover, provides hands on experience on isolation, characterization, mass multiplication and application of biofertilizer and biopesticides, respectively. This domain mainly familiarizes the students in management of inputs in organic farms and helps them to become a skilled professional after successful completion
Domain Track: Organic Farming
Course Attendees
Still no participant
Course Reviews
Still no reviews
Domain-organic farming is an integration of skill and knowledge that aims to impart traditional, innovative and scientific skills to students in organic farming and provide a practical know-how on production of low cost organic inputs, bio-fertilizers and bio-pesticides. Upon successful completion students will be able to acquire skill onTrack Total Credits ( T-P-P): 3-15-11 (29 credits)
Courses Division:
Practice Courses: 09 credits
AELP Linked with Domain: 11 credits
Domain track objectives:
Domain Learning Outcomes:
Reference Books:
Career Scope:
Domain Syllabus:
Track courses:
1. Organic Farming. (1-2-0)
Theory:
- Module 1.1: Organic Farming: Principles, Developing Organic farm, Conversion of Soil to Organic.
- Module 1.2: Soil Cultivation and Tillage: Creating good growing conditions, Minimum disturbance, Soil compaction, and Types of Soil Cultivation.
- Module 1.3: Crop Planning and Management: Crop rotation, Intercropping, Cover crops, Crop- Animal association, Designing cropping systems.
- Module 1.4: Mulching: Selection of Mulch materials, Source of Mulching materials, Recommendation while using Mulches, Application of Mulch.
- Module 1.5: Organically Manage: Live fencing, Water, Nutrient, Weed, Pest and Disease.
- Module 1.6: Plant Propagation: Criteria for Seed evaluation, characterization and multiplication, Importance of Traditional Varieties, Seed conservation and its Certification.
- Module 1.7: Animal Husbandry: Animal Housing, Animal Feeding, Animal Health, Breeding Goals.
- Module 1.8: Introduction of Forest Trees: Azadirachta indica, Pongamia pinnata, Tamarindus indica, Sesbania grandiflora, Dalbergia latifolia, Terminalia chebula etc.
- Module 1.9: ITKs of Gajapati: Collection, Study and Implementation.
- Module 1.10: Other forms of Organic Management: Biodynamic Agriculture, Rishi Krishi, Natural Farming, Panchgavya Krishi, Natueco Farming. Homa Farming and EM-Technology.
- Practical:
- Practical 1.1: Preparation of Enrich Compost.
- Practical 1.2: Preparation of Vermicompost.
- Practical 1.3: Preparation of Green manures, Liquid manures, Panchgavya, Biodynamic and NADEP.
- Practical 1.4: Preparation of different organic Insecticides/ Pesticides.
- Practical 1.5: Identification and use of Mulch materials.
- Practical 1.6: Water Management
- Practical 1.7: Weed Management.
- Practical 1.8: Seed Multiplication, conservation and Certification process.
- Practical 1.9: Practical on Animal Husbandry.
- Practical 1.10: Collection of ITKs.
- Practical 1.11: Practical on Conversion of Soil to Organic
2. Certification and Inspection Systems in Organic Farming in India. (1-2-0)
Theory:
- Module 2.1: Organic Certification: The Certification Process, Certification and Product Labelling, Certification around the World.
- Module 2.2: Regulatory Mechanism for Organic Certification in India: Scope and Operational Structure of National Programme for Organic Production.
- Module 2.3: National Standards for Organic Production: Conversion requirements, Maintenance of Organic Management, Crop Production, Animal Husbandry, Food Processing and Handling, Labelling, Storage and Transport.
- Module 2.4: Inspection and Certification Process:
- Inspection and Certification Agency.
- Annual Surveillance and Review of Inspection and Certification Agencies.
- Inspection and Assignments.
- Inspection visit and Reports.
- Methods and Frequency.
- Analysis and Residue Testing.
- Inspection Regime for Part Conversion and Parallel Production. Inspection for use of Genetically Engineered Products.
- Inspection and Certification of Grower Group.
- Procedure for Implementation of Internal Control System.
- Certification Process.
- Mandatory checks to be undertaken by the Authorized Inspection and Certification Agency during Inspection.
Practical:
- To Visit and Document on
- Practical 2.1: Different Organic certification Agencies in Odisha.
- Practical 2.2: Hands on learning on Packaging & Labelling.
- Practical 2.3: Organic Cold Storage in Odisha.
- Practical 2.4: Certified Organic Farmer.
- Practical 2.5: Certified Organic Grower group.
- Practical 2.6: Food Processing & Handling Unit.
- Practical 2.7: Animal Husbandry Unit
3. Biopesticides and Biofertilizers. (1-2-0)
Theory:
- Module 3.1: Introduction, status and scope.
- Module 3.2: Concepts and classification of biopesticides viz. pathogen, botanical pesticides and biorationales.
- Module 3.3: Botanicals and their uses.
- Module 3.4: Mass production technology of bio-pesticides Virulence, Pathogenicity and symptoms of entomopathogenic pathogens and nematodes.
- Module 3.5: Methods of application of biopesticides. Methods of quality control and Techniques of biopesticides. Impediments and limitation in production and use of biopesticide..
- Module 3.6: Introduction, status and scope.
- Module 3.7: Structure and characteristic features of bacterial biofertilizers- Azospirillum, Azotobacter, Bacillus, Pseudomonas, Rhizobium and Frankia.
- Module 3.8: Cynobacterial biofertilizers: Anabaena, Nostoc and Hapalosiphon.
- Module 3.9: Fungal biofertilizers: AM mycorrhiza and ectomycorhiza.
- Module 3.10: Nitrogen fixation: Free living and symbiotic nitrogen fixation, process of nodule formation, role of different genes (Nod and Nif), enzymes and Bio chemistry of Nitrogen fixation.
- Module 3.11: P-Solubilizer and K-mobilizer: Mechanism of P- solubilization, phosphate mobilization and K solubilisation.
- Module 3.12: Production Technology: Strain selection, sterilization, growth and fermentation, mass production of carrier based, liquid biofertilizers and EM.
- Module 3.13: FCO specifications and quality control of biofertilizers.
- Module 3.14: Application: Soil, Seeds, Seedlings and Tubers etc.
- Module 3.15: Biofertilizers: Factors influencing the efficacy of biofertilizers, Storage, Shelf life, Quality control, Certification and marketing.
Practical:
- Practical 3.1: Hands-on Training on Laboratory Equipments
- Practical 3.2: Isolation and purification of Azospirillum.
- Practical 3.3: Isolation and Purification of Azotobacter.
- Practical 3.4: Isolation and Purification of Rhizobium.
- Practical 3.5: Isolation and Purification of P-solubilizers.
- Practical 3.6: Isolation and Purification of cyanobacteria.
- Practical 3.7: Isolation of AM fungi by Wet sieving method.
- Practical 3.8: Isolation and Purification by sucrose gradient method.
- Practical 3.9: Isolation and purification of Trichoderma.
- Practical 3.10: Isolation and purification of Pseudomonas.
- Practical 3.11: Isolation and purification of Bacillus.
- Practical 3.12: Isolation and purification of Metarhyzium.
- Practical 3.13: Layout of Bio fertilizer Laboratory.
- Practical 3.14: Layout of Bio pesticide Laboratory.
- Practical 3.15: Market Survey and Marketing.
Practice courses:
1. Organic Production- Field Crops. (0-3-0)
Practice:
- Practice 1.1: Components: Organic farm.
- Practice 1.2: Implement: Conversion of Soil to Organic.
- Practice 1.3: Seed: Multiplication of Adopted and Resistant Varieties, Conservation and Certification.
- Practice 1.4: Water Management: Reduce evaporation, Increasing Infiltration, Planting Pits, Contour bunds, Catchment strips, Drip irrigation systems and Water Storage.
- Practice 1.5: Organic Nutrient production, Analysis and its Application: Green manures, Liquid manures, Panchgavya, Biodynamic, NADEP and Vermicompost etc.
- Practice 1.6: Organic Pesticides production, Analysis and its Application: Neemashtra, Agniashtra, Brahmashtra, Jeevamrutam and Neem Oil etc.
- Practice 1.7: Weed Management.
- Practice 1.8: Harvest and Post-Harvest Management.
- Practice 1.9: Formulating Good Agricultural Practice (GAP).
- Practice 1.10: Field trials of ITK’s to assess their effectiveness (Gajapati context).
- Practice 1.11: Hazard analysis and Critical Control Point. Documentation for certification.
- Practice 1.12: Visit to Organic farm/field.
2. Organic Production- Horticultural Crops. (0-3-0)
Practice:
- Practice 2.1: Field Preparation.
- Practice 2.2: Selection of Adopted and Resistant Varieties.
- Practice 2.3: Seed Treatment.
- Practice 2.4: Raising of Seedling and Nursery Management.
- Practice 2.5: Mulching.
- Practice 2.6: Identification and Use: Natural Plant Growth Regulators and Micronutrients.
- Practice 2.7: Management: Water, Nutrient, Weed, Pest and Disease
- Practice 2.8: Harvest and Post-Harvest Management.
- Practice 2.9: Visit to Organic fields and marketing centers.
3. Biofertilizer and Biopesticide Production Technology. (0-3-0)
Practice:
- Practice 3.1: Isolation and purification of important biopesticides.
- Practice 3.2: Mass multiplication of Trichoderma Pseudomonas, Bacillus, Metarhyzium etc. and its production.
- Practice 3.3: Identification of important botanicals.
- Practice 3.4: Field visit to explore naturally infected cadavers.
- Practice 3.5: Identification of entomopathogenic entities in field condition.
- Practice 3.6: Quality control of biopesticides.
- Practice 3.7: Visit to biopesticide laboratory in nearby area.
- Practice 3.8: Isolation and purification of Azospirillum, Azotobacter, Rhizobium, P-solubilizers and cyanobacteria.
- Practice 3.9: Mass multiplication and inoculums production of biofertilizers.
- Practice 3.10: Isolation of AM fungi by Wet sieving method and sucrose gradient method.
- Practice 3.11: Mass production of AM inoculants
AELP Linked with Domain (0-0-11).
- Scaling Production and Marketing
- Field Trials (Gajapati context)
- Project Based Learning
- Publication
Track courses:
Track courses:
1. Organic Farming. (1-2-0)
Theory:
- Module 1.1: Organic Farming: Principles, Developing Organic farm, Conversion of Soil to Organic.
- Module 1.2: Soil Cultivation and Tillage: Creating good growing conditions, Minimum disturbance, Soil compaction, and Types of Soil Cultivation.
- Module 1.3: Crop Planning and Management: Crop rotation, Intercropping, Cover crops, Crop- Animal association, Designing cropping systems.
- Module 1.4: Mulching: Selection of Mulch materials, Source of Mulching materials, Recommendation while using Mulches, Application of Mulch.
- Module 1.5: Organically Manage: Live fencing, Water, Nutrient, Weed, Pest and Disease.
- Module 1.6: Plant Propagation: Criteria for Seed evaluation, characterization and multiplication, Importance of Traditional Varieties, Seed conservation and its Certification.
- Module 1.7: Animal Husbandry: Animal Housing, Animal Feeding, Animal Health, Breeding Goals.
- Module 1.8: Introduction of Forest Trees: Azadirachta indica, Pongamia pinnata, Tamarindus indica, Sesbania grandiflora, Dalbergia latifolia, Terminalia chebula etc.
- Module 1.9: ITKs of Gajapati: Collection, Study and Implementation.
- Module 1.10: Other forms of Organic Management: Biodynamic Agriculture, Rishi Krishi, Natural Farming, Panchgavya Krishi, Natueco Farming. Homa Farming and EM-Technology.
- Practical:
- Practical 1.1: Preparation of Enrich Compost.
- Practical 1.2: Preparation of Vermicompost.
- Practical 1.3: Preparation of Green manures, Liquid manures, Panchgavya, Biodynamic and NADEP.
- Practical 1.4: Preparation of different organic Insecticides/ Pesticides.
- Practical 1.5: Identification and use of Mulch materials.
- Practical 1.6: Water Management
- Practical 1.7: Weed Management.
- Practical 1.8: Seed Multiplication, conservation and Certification process.
- Practical 1.9: Practical on Animal Husbandry.
- Practical 1.10: Collection of ITKs.
- Practical 1.11: Practical on Conversion of Soil to Organic
2. Certification and Inspection Systems in Organic Farming in India. (1-2-0)
Theory:
- Module 2.1: Organic Certification: The Certification Process, Certification and Product Labelling, Certification around the World.
- Module 2.2: Regulatory Mechanism for Organic Certification in India: Scope and Operational Structure of National Programme for Organic Production.
- Module 2.3: National Standards for Organic Production: Conversion requirements, Maintenance of Organic Management, Crop Production, Animal Husbandry, Food Processing and Handling, Labelling, Storage and Transport.
- Module 2.4: Inspection and Certification Process:
- Inspection and Certification Agency.
- Annual Surveillance and Review of Inspection and Certification Agencies.
- Inspection and Assignments.
- Inspection visit and Reports.
- Methods and Frequency.
- Analysis and Residue Testing.
- Inspection Regime for Part Conversion and Parallel Production. Inspection for use of Genetically Engineered Products.
- Inspection and Certification of Grower Group.
- Procedure for Implementation of Internal Control System.
- Certification Process.
- Mandatory checks to be undertaken by the Authorized Inspection and Certification Agency during Inspection.
Practical:
- To Visit and Document on
- Practical 2.1: Different Organic certification Agencies in Odisha.
- Practical 2.2: Hands on learning on Packaging & Labelling.
- Practical 2.3: Organic Cold Storage in Odisha.
- Practical 2.4: Certified Organic Farmer.
- Practical 2.5: Certified Organic Grower group.
- Practical 2.6: Food Processing & Handling Unit.
- Practical 2.7: Animal Husbandry Unit
3. Biopesticides and Biofertilizers. (1-2-0)
Theory:
- Module 3.1: Introduction, status and scope.
- Module 3.2: Concepts and classification of biopesticides viz. pathogen, botanical pesticides and biorationales.
- Module 3.3: Botanicals and their uses.
- Module 3.4: Mass production technology of bio-pesticides Virulence, Pathogenicity and symptoms of entomopathogenic pathogens and nematodes.
- Module 3.5: Methods of application of biopesticides. Methods of quality control and Techniques of biopesticides. Impediments and limitation in production and use of biopesticide..
- Module 3.6: Introduction, status and scope.
- Module 3.7: Structure and characteristic features of bacterial biofertilizers- Azospirillum, Azotobacter, Bacillus, Pseudomonas, Rhizobium and Frankia.
- Module 3.8: Cynobacterial biofertilizers: Anabaena, Nostoc and Hapalosiphon.
- Module 3.9: Fungal biofertilizers: AM mycorrhiza and ectomycorhiza.
- Module 3.10: Nitrogen fixation: Free living and symbiotic nitrogen fixation, process of nodule formation, role of different genes (Nod and Nif), enzymes and Bio chemistry of Nitrogen fixation.
- Module 3.11: P-Solubilizer and K-mobilizer: Mechanism of P- solubilization, phosphate mobilization and K solubilisation.
- Module 3.12: Production Technology: Strain selection, sterilization, growth and fermentation, mass production of carrier based, liquid biofertilizers and EM.
- Module 3.13: FCO specifications and quality control of biofertilizers.
- Module 3.14: Application: Soil, Seeds, Seedlings and Tubers etc.
- Module 3.15: Biofertilizers: Factors influencing the efficacy of biofertilizers, Storage, Shelf life, Quality control, Certification and marketing.
Practical:
- Practical 3.1: Hands-on Training on Laboratory Equipments
- Practical 3.2: Isolation and purification of Azospirillum.
- Practical 3.3: Isolation and Purification of Azotobacter.
- Practical 3.4: Isolation and Purification of Rhizobium.
- Practical 3.5: Isolation and Purification of P-solubilizers.
- Practical 3.6: Isolation and Purification of cyanobacteria.
- Practical 3.7: Isolation of AM fungi by Wet sieving method.
- Practical 3.8: Isolation and Purification by sucrose gradient method.
- Practical 3.9: Isolation and purification of Trichoderma.
- Practical 3.10: Isolation and purification of Pseudomonas.
- Practical 3.11: Isolation and purification of Bacillus.
- Practical 3.12: Isolation and purification of Metarhyzium.
- Practical 3.13: Layout of Bio fertilizer Laboratory.
- Practical 3.14: Layout of Bio pesticide Laboratory.
- Practical 3.15: Market Survey and Marketing.
Practice courses:
1. Organic Production- Field Crops. (0-3-0)
Practice:
- Practice 1.1: Components: Organic farm.
- Practice 1.2: Implement: Conversion of Soil to Organic.
- Practice 1.3: Seed: Multiplication of Adopted and Resistant Varieties, Conservation and Certification.
- Practice 1.4: Water Management: Reduce evaporation, Increasing Infiltration, Planting Pits, Contour bunds, Catchment strips, Drip irrigation systems and Water Storage.
- Practice 1.5: Organic Nutrient production, Analysis and its Application: Green manures, Liquid manures, Panchgavya, Biodynamic, NADEP and Vermicompost etc.
- Practice 1.6: Organic Pesticides production, Analysis and its Application: Neemashtra, Agniashtra, Brahmashtra, Jeevamrutam and Neem Oil etc.
- Practice 1.7: Weed Management.
- Practice 1.8: Harvest and Post-Harvest Management.
- Practice 1.9: Formulating Good Agricultural Practice (GAP).
- Practice 1.10: Field trials of ITK’s to assess their effectiveness (Gajapati context).
- Practice 1.11: Hazard analysis and Critical Control Point. Documentation for certification.
- Practice 1.12: Visit to Organic farm/field.
2. Organic Production- Horticultural Crops. (0-3-0)
Practice:
-
- Practice 2.1: Field Preparation.
- Practice 2.2: Selection of Adopted and Resistant Varieties.
- Practice 2.3: Seed Treatment.
- Practice 2.4: Raising of Seedling and Nursery Management.
- Practice 2.5: Mulching.
- Practice 2.6: Identification and Use: Natural Plant Growth Regulators and Micronutrients.
Practice 2.7: Management: Water, Nutrient, Weed, Pest and Disease
- Practice 2.8: Harvest and Post-Harvest Management.
- Practice 2.9: Visit to Organic fields and marketing centers.
3. Biofertilizer and Biopesticide Production Technology. (0-3-0)
Practice:
- Practice 3.1: Isolation and purification of important biopesticides.
- Practice 3.2: Mass multiplication of Trichoderma Pseudomonas, Bacillus, Metarhyzium etc. and its production.
- Practice 3.3: Identification of important botanicals.
- Practice 3.4: Field visit to explore naturally infected cadavers.
- Practice 3.5: Identification of entomopathogenic entities in field condition.
- Practice 3.6: Quality control of biopesticides.
- Practice 3.7: Visit to biopesticide laboratory in nearby area.
- Practice 3.8: Isolation and purification of Azospirillum, Azotobacter, Rhizobium, P-solubilizers and cyanobacteria.
- Practice 3.9: Mass multiplication and inoculums production of biofertilizers.
- Practice 3.10: Isolation of AM fungi by Wet sieving method and sucrose gradient method.
- Practice 3.11: Mass production of AM inoculants
AELP Linked with Domain (0-0-11).
- Scaling Production and Marketing
- Field Trials (Gajapati context)
- Project Based Learning
- Publication
Track courses:
1. Organic Farming (1-2-0): Theory and Practical: Session Plan
- Session 1.1: Organic Farming: Principles, Developing Organic farm, Conversion of Soil to Organic.
- Practical 1: Practical on Conversion of Soil to Organic.
- Organic Farming Module-1...

- Video- Principles...

- Session 2:Soil Cultivation and Tillage: Creating good growing conditions, Minimum disturbance and Soil compaction and Types of Soil Cultivation.
- Practical 1.2: Ploughing with Country plough, field level understanding of Physical nature of Soil for Crop growth.
- Organic Farming Module-2...

- Document- Tillage...

- Video- Soil Compaction...

- Land Preparation 1...

- Land Preparation 2...

- Ploughing...

- Session 1.3: Crop Planning and Management: Crop rotation, Intercropping, Cover crops, Crop- Animal association, designing cropping systems.
- Practical 3: Raising of Crops with different Cropping systems.
- Organic Farming Module-3...

- Video- Crop rotation 1...

- pdf- Crop rotation 2...

- pdf- Cropping System...

- Video- Multiple Cropping 1...

- Video- Multiple Cropping 2...

- Document- Crop Rotation 3
- Session 1.4:Mulching: Selection of Mulch materials, Source of Mulching materials, Recommendation while using Mulches, Application of Mulch.
- Pratical 4: Identification and use of Mulch materials.
- Organic Farming Module-4...

- Session 1.5: Organically Manage: Live fencing and Water, Nutrient, Weed, Pest and Disease.
- Practical 5: Identification and Multiplication of Live fencing Plants, Preparation of Enrich Compost, Vermicompost, organic Insecticides/ Pesticides.
- Organic Farming Module-5...

- Video- Weed...

- Video- Nutrient Management...

- Video - Integrated Nutrient Management...

- Video- Pest Management...

- Visit site for Manure study materials (Wageningen University)
- Video- Live Fence...

- Video- Live Fence 2...

- Video-Water management 1...

- Video-Water management 2...

- Session 1.6:Plant Propagation: Criteria for Seed evaluation and characterization.
- Importance and Multiplication of Traditional Varieties, Seed conservation and its Certification
- Practical 6: Seed Multiplication, conservation and Certification process.
- Organic Farming Module-6...

- Visit Seed Center of Wageningen University
- Session 1.7:Animal Husbandry: Animal Housing, Animal Feeding, Animal Health, Breeding Goals.
- Practical 7: Designing Animal Shed, Organic Feed Formulation, Visit to Animal Husbandary Farm.
- Organic Farming Module-7...

- Session 1.8: Introduction of Forest Trees: Azdirachta indica, Pongamia pinnata, Tamarindus indica, Sesbania grandiflora, Dalbergia latifolia, Terminalia chebula etc.
- Practical 8: Identification and Multiplication of Forest Trees
- Organic Farming Module-8...

- Session 1.9: ITKs of Gajapati: Collection, Study and Implementation.
- Practical 9: Collection of ITKs.
- Organic Farming Module-9...

- Session 1.10:Other forms of Organic Management: Biodynamic Agriculture, Rishi Krishi and Natural Farming, Panchgavya Krishi, Natueco Farming. Homa Farming and EM-Technology.
- Practical 10: Preparation of Green manures, Liquid manures, Panchgavya, Biodynamic and NADEP
- Organic Farming Module-10...

2. Certification and Inspection Systems in Organic Farming in India (1-2-0): Theory and Practical: Session Plan
- Session 2.1:Organic Certification: The Certification Process.Certification and Product Labelling, Certification around the World.
- Practical 1: To visit and document different Organic certification Agencies in Odisha.
- certification Module-1...

- Session 2.2: Regulatory Mechanism for Organic Certification in India: Scope and Operational Structure of National Programme for Organic Production.
- Practical 2: Hands on learning on Packaging & Labelling.
- certification Module-2...

- Session 2.3: National Standards for Organic Production: Conversion requirements and Maintenance of Organic Management.
- Practical 3: Visit to Certified Organic Farmer for doumentation.
- certification Module-3...

- Session 2.4:National Standards for Organic Production: Crop Production.
- Practical 4: Visit and document to Certified Organic Grower group
- certification Module-3...

- Session 2.5:National Standards for Organic Production: Animal Husbandry.
- Practical 5: To visit and document in Animal Husbandry Unit.
- certification Module-3...

- Session 2.6:National Standards for Organic Production: Food Processing and Handling.
- Practical 6: To visit and document in Food Processing & Handling Unit.
- certification Module-3...

- Session 2.7:National Standards for Organic Production: Labelling, Storage and Transport.
- Practical 6: To visit and document Organic Cold Storage in Odisha.
- certification Module-3...

- Session 2.8:Inspection and Certification Process: Inspection and Certification Agency, Annual Surveillance and Review of Inspection and Certification Agencies.
- Practical 7: To document and understand the compliance standards.
- certification Module-4...

- Session 2.9: Inspection and Certification Process: Inspection and Assignments, Inspection visit and Reports, Methods and Frequency.
- Practical 8: To document and understand the compliance standards.
- certification Module-4...

- Session 2.10:Inspection and Certification Process: Analysis and Residue Testing, Inspection Regime for Part Conversion and Parallel Production.
- Pratical 9: To document and understand the compliance standards.
- certification Module-4...

- Session 10:Inspection and Certification Process: Inspection for use of Genetically Engineered Products, Inspection and Certification of Grower Groups.
- Practical 10: To document and understand the compliance standards.
- certification Module-4...

3. Biopesticides and Biofertilizers (1-2-0): Theory and Practical: Session Plan
- Session 3.1: Introduction, status and scope. Concepts and classification of biopesticides
- Practical 1: Hands on Training on laboratory equipment and Layout of Biopesticides laboratory.
- Video
- PDF1....

- Session 3.2: Pathogen, Botanical pesticides. biorationales. Botanicals and their uses.
- Practical 2: Identification of some important botanicals.
- Video...

- PDF2....

- Session 3.3: Mass production technology of bio-pesticides.
- Practical 3: Process involved in the Production of Biopesticides.
- Video...

- PDF3....

- Session 3.4: Virulence, Pathogenicity and symptoms of entomopathogenic pathogens and nematodes.
- Practical: Identification of Pathogens and nematodes used as bio pesticides.
- Video...

- PDF4. ...

- Session 3.5: Methods of application of biopesticides. Methods of quality control and Techniques of biopesticides. Impediments and limitation in production and use of biopesticide.
- Practical 5: Methods of application of biopesticides.
- Video...

- PDF5. ...

- Session 3.6: Biofertilizer- Introduction, status and scope.
- Practical 6: Hands on Training on Laboratory Equipments and Layout of Biofertilizer Laboratory.
- Video...

- Introduction and Structure of Biofertilizers ...

- Session 3.7: Structure and characteristic features of bacterial biofertilizers- Azospirillum, Azotobacter, Bacillus, Pseudomonas, Rhizobium and Frankia; Cynobacterial biofertilizers: Anabaena, Nostoc and Hapalosiphon. Fungal biofertilizers: AM mycorrhiza and ectomycorhiza.
- Practical 7: Isolation and Purification of Azospirillum, Azotobacter, Bacillus, Pseudomonas, Rhizobium and Frankia; Cynobacterial biofertilizers: Anabaena, Nostoc and Hapalosiphon. Fungal biofertilizers: AM mycorrhiza and ectomycorhiza.
- Video 1...

- Video 2...

- Video 3...

- Video 4...

- Video 5...

- Write up on Practical...

- Introduction and Structure of Biofertilizers...

- Structure of Biofertizers
- Session 3.8: Nitrogen fixation: Free living and symbiotic nitrogen fixation, Process of Nodule formation, Role of different Genes (Nod and Nif), Enzymes and Biochemistry of Nitrogen Fixation.
- Practical 8:
- Video...

- Write up on Practical...

- Nitrogen Fixation...

- Session 3.9: P- solubilizer and K- mobilizer: Mechanism of phosphate solubilization, phosphate mobilization and K solubilization.
- Pratical 9: Isolation and Purification of P- solubilizers and K- mobilizers.
- Video...

- Write up on Practical...

- P and K Solubilizers...

- Session 3.10: Production Technology: Strain selection, sterilization, growth and fermentation, mass production of carrier based, liquid biofertilizers and EM. FCO specifications and quality control of biofertilizers.Soil, Seeds, Seedlings and Tubers etc. Factors influencing the efficacy of biofertilizers, Storage, Shelf life, Quality control, Certification and marketing.
- Practical 10: Mass Production, Market Survey and Marketing of Biofertilizers.
- Video 1...

- Video 2...

- Video 3...

- Video 4...

- Video 5...

- Write up on Practical...

- Mass Biofertizers Production...

Practice courses:
1. Organic Production- Field Crops (0-3-0): Practice: Session Plan
- Practice 1.1: Components: Organic farm, Conversion of Soil to Organic.
- Practice 1.2: Seed: Multiplication of Adopted and Resistant Varieties, Conservation and Certification.
- Practice 1.3: Water Management: Reduce evaporation, Increasing Infiltration, Planting Pits, Contour bunds, Catchment strips, Drip irrigation systems and Water Storage.
- Practice 1.4: Organic Nutrient production, Analysis and its Application: Green manures, Liquid manures, Panchgavya, Biodynamic, NADEP and Vermicompost etc.
- Practice 1.5: Organic Pesticides production, Analysis and its Application: Neemashtra, Agniashtra, Brahmashtra, Jeevamrutam and Neem Oil etc.
- Practice 1.6: Application of different methods to Manage Weeds.
- Practice 1.7: Harvest and Post-Harvest Management.
- Practice 1.8: Formulating Good Agricultural Practice (GAP).
- Practice 1.9: Field trials of ITK’s to assess their effectiveness (Gajapati context).
- Practice 1.10: Hazard analysis and Critical Control Point. Documentation for certification.
2. Organic Production: Horticultural Crops (0-3-0): Practice: Session Plan
Practice 2.1: Field Preparation.
- Practice 2.2: Selection of Adopted and Resistant Varieties.
- Session 2.3: Seed Treatment.
- Practice 2.4: Raising of Seedling and Nursery Management.
- Practice 2.5: Mulching
- Practice 2.6: Identification and Use: Natural Plant Growth Regulators and Micronutrients.
- Practice 2.7: Management: Water, Nutrient, Weed, Pest and Disease
- Practice 2.8: Harvest and Post-Harvest Management.
- Practice 2.9: Visit to Organic fields and marketing centers.
3. Biofertilizer and Biopesticide Production Technology (0-3-0): Practice: Session Plan
- Practice 3.1: Isolation and Purification of important Biopesticides.
- Practice 3.2: Mass multiplication of Trichoderma Pseudomonas, Bacillus, Metarhyzium etc. and its production.
- Video...

- Practice 3.3: Identification of important Botanicals.
- Video...

- Practice 3.4: Isolation and purification of Azospirillum, Azotobacter, Rhizobium, P-solubilizers and cyanobacteria.
- Video 1...

- Video 2...

- Video 3...

- Video 4...

- Practice 3.5: Mass multiplication and inoculums production of biofertilizers.
- Video...

- Practice 3.6: Isolation of AM fungi by Wet sieving method and sucrose gradient method.
- Video...

- Practice 3.7: Mass production of AM inoculants.
- Video...

- Practice 3.8: Field visit to explore naturally infected cadavers.
- Practice 3.9: Identification of entomopathogenic entities in field condition.
- Video...

- Practice 3.10: Visit to biopesticide laboratory in nearby area.
A. List of Projects/ Case Studies to be taken up under Organic Farming Domain:
- Farmers Market
- Biofertilizer Production in Odisha and Andhra Pradesh.
- FPOs
- ITKs
- Organic Grower in Odisha and Andhra Pradesh.
B. Scaling Production:
- Higher Production.
- Awareness Program.
- Marketing
C. Field Trials (Gajapati Context):
- Application.
- Generates Results.
- Publications.
- Supports Awareness and Mobilization.
Media

Our Main Teachers

A doctorate in Soil Science and Agricultural Chemistry, He is a dynamic professional with versatile exposure in academics, research and extension. He had a vast experience in organic agriculture both in practice as well as promotion across Odisha through various NGO partners. Mobile: 8144297933 Email: [email protected]

An experienced Bio-Medical Science Professional with 16 years of experience and strong academic background, having completed Masters and Doctorate in Biotechnology. He worked as an Assistant Professor in Department of Biotechnology, Roland Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Berhampur, Orissa, India and acted as a visiting Faculty for the Dept. of Biotechnology, Berhampur University, Orissa. He also […]

He is presently working as an Assistant Professor in Department of Agronomy and Agroforestry at M.S. Swaminathan School of Agriculture, Centurion University of Technology and Management. He is specialized in crop husbandry and had research experience in nutrient management using precision tools. Besides, he even published more than 20 research as well as review articles […]

A doctorate from G. B. Pant University of Agriculture and Technology. Presently, working An Assistant Professor in Department of Plant Pathology at M.S. Swaminathan School of Agriculture, Centurion University of Technology and Management. He is specialized in plant disease epidemiology and plant virology. Mobile: 9446659706 Email: [email protected]

An Assistant Professor in Department of Horticulture at M.S. Swaminathan School of Agriculture, Centurion University of Technology and Management. She is specialized in genetic variability and hybridization in citrus. She had more than 5 years of experience in cultivation of horticultural crops through organic management both under open and controlled conditions.